Pulumi ESC (Environments, Secrets, and Configuration)
Pulumi ESC (Environments, Secrets, and Configuration) allows teams to tackle secrets and configuration complexity for modern cloud environments, alleviating maintenance burden and reducing costly mistakes, and creating a “secure by default” posture. Pulumi ESC is a new category of configuration as code product, motivated by our experience working with hundreds of Pulumi IaC customers to address their needs in managing secrets and configuration at scale within their Pulumi infrastructure and across other cloud applications and infrastructure projects.
Pulumi ESC enables teams to aggregate secrets and configuration from many sources into a composable collection called an environment. Teams can then consume those configuration and secrets from a variety of different infrastructure and application services. Pulumi ESC works hand-in-hand with Pulumi IaC to simplify configuration management, as well as a standalone CLI and API for other use cases apart from Pulumi IaC.
Pulumi ESC is offered as a fully managed cloud service in Pulumi Cloud (and Pulumi Cloud Self-hosted in the near future). The pulumi/esc project is open source, and contains the evaluation engine for environments, the esc CLI, and in the future, the extensible plugins for source and target integrations.
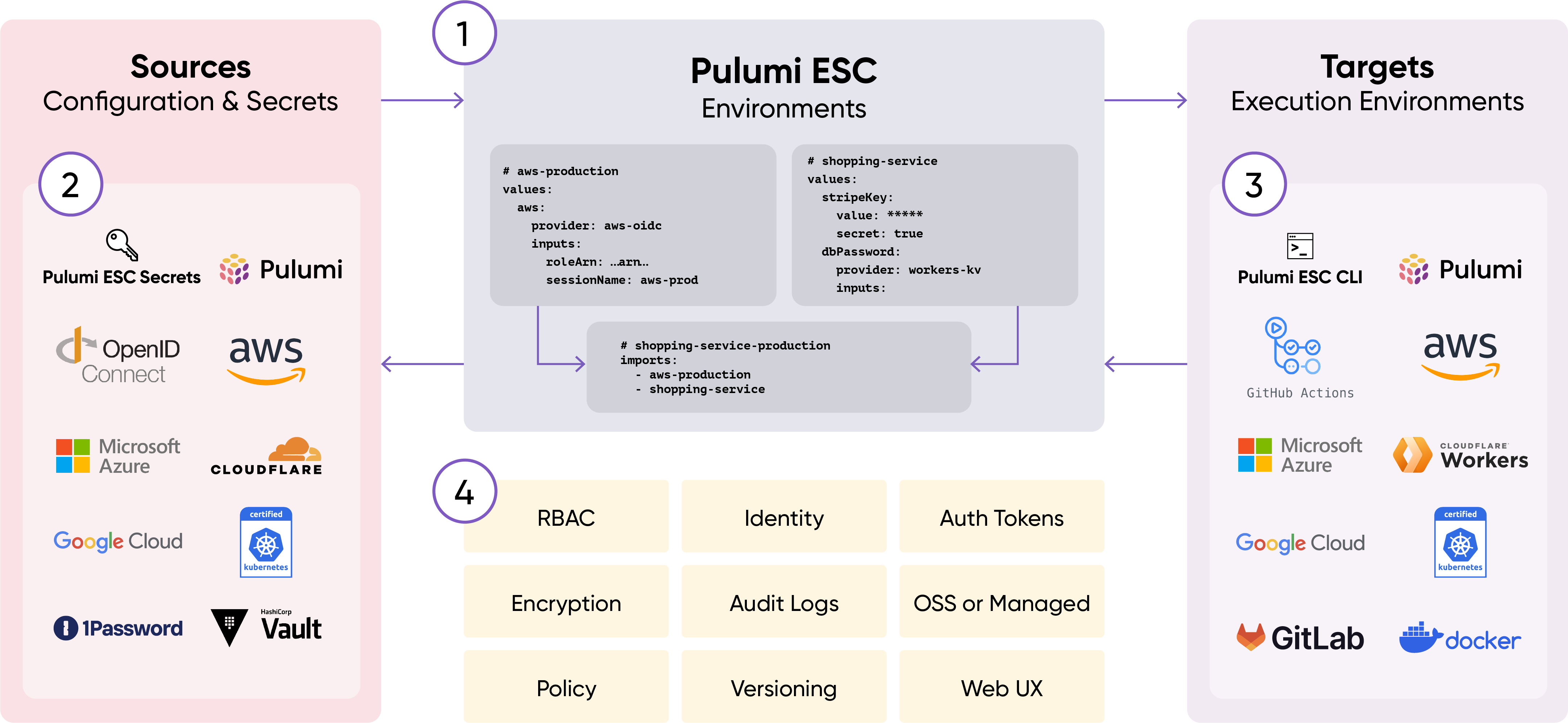
The following details corresponds to the numbered sections in the above diagram:
Pulumi ESC enables you to define environments, which contain collections of secrets and configuration. Each environment can be composed from multiple environments.
Pulumi ESC supports a variety of configuration and secrets sources, and it has an extensible plugin model that allows third-party sources.
Pulumi ESC has a rich API that allows for easy integration. Every value in an environment can be accessed from any target execution environment.
Every environment can be locked down with RBAC, versioned, and audited.
Dynamic Secrets Providers
Support for dynamic configuration providers allow Pulumi ESC to integrate with secrets stored in any other provider. Organizations often use AWS OIDC, AWS Secrets Manager, Vault, Azure OIDC, Azure KeyVault, GCP OIDC, and GCP Secrets Manager plus many more sources of truth for their secrets and configuration. Pulumi ESC supports them all, providing a single interface to your configuration and secrets, no matter where their source of truth is. Pulumi ESC works with these tools to provide improved management of secrets and configuration.
Teams can setup OIDC in their cloud providers to allow Environments to retrieve dynamic short-lived credentials. They can also pull secrets from other secrets managers and vaults.
These credentials can be used with Pulumi IaC with pulumi up as well as used to run external CLIs like aws, kubectl, and more.
Composable
Platform and service teams can centralize and control common configuration and secrets by creating environments that other teams can import. They can trace what other environments or stacks are using their configuration and assess the blast radius of any changes.
Configuration as Code
Environments are defined as YAML documents which can describe how to project and compose secrets and configuration, integrate dynamic configuration providers, and compute new configuration from other values (constructing a URL from a DNS name, or concatenating multiple configuration values into a derived value). The incredible flexibility of a code-based approach over traditional point-and-click interfaces allows Pulumi ESC to offer rich expressiveness for managing complex configuration.
Authentication and RBAC
Pulumi ESC brokers access to secrets and configuration that live in other systems, and so authentication and granular RBAC are critical to ensure robust access controls across your organization. Pulumi ESC leverages the same Pulumi Cloud identity, RBAC, Teams, SAML/SCIM and scoped access tokens that are used for Pulumi IaC today, extending these all to managing access to environments as well as Stacks.
Teams can create and control access to their environments. They can control who can update and preview environments, as well as who can open environments and retrieve their secrets. Audit logs let teams know who has changed or accessed configuration.
Auditable
Environments must be “opened” to compute and see the set of value they provide, and this action is recorded in audit logs, including a full record of how each value was sourced from within the hierarchy of environments that contributed to it.
Consume from Anywhere
The esc CLI and the Pulumi ESC Rest API enables environments to be accessed from any application, infrastructure provider, or automation system. At launch, first-class integrations are available with Pulumi IaC, local environment and .env files, GitHub Actions, and more.
Detailed overview of environments
Learn more about managing environments using Pulumi ESC.
Getting Started with Pulumi ESC
Begin your journey with Pulumi ESC through a hands-on, self-paced tutorial.
Pulumi ESC CLI overview
Please see ESC CLI overview for details on interacting with environments using the command line.
Syntax Reference
The Pulumi ESC Syntax Reference documentation shows examples of simple and complex configuration, imports, and common provider integrations.
Thank you for your feedback!
If you have a question about how to use Pulumi, reach out in Community Slack.
Open an issue on GitHub to report a problem or suggest an improvement.
